|
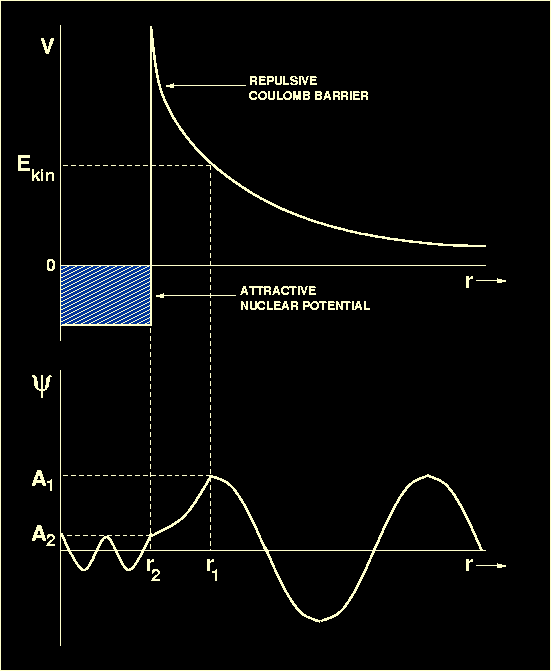
Figure 15:
|
Upper panel: A schematic plot of the potential energy
V (i.e. the energy which one nucleus must have in order
to approach another nucleus)
versus separation between two nuclei. At large separations, the electrostatic
repulsion
dominates. For separations of r<10-15m, the strong
nuclear force takes over, allowing the two nuclei to fuse. Lower panel:
A schematic plot of the wave function
representing the penetration of a potential barrier by a nucleus
whose kinetic energy of approach
Ekin is below that of the barrier. The wave function
oscillates sinusoidally in the inner and outer classically allowed regions
and decays exponentially in the intervening classically forbidden region.
|